We publish electronic versions of “Reliability Ques” periodically as a means of keeping our community up-to-date on effective tools, techniques, and approaches to improving the reliability, maintainability, and quality of products and systems.
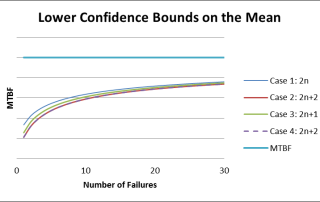
Confidence Bounds on the Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) for a Time-Truncated Test
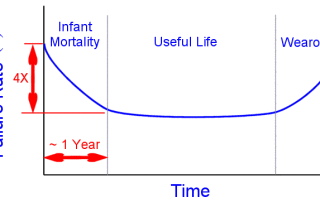
Maintenance Planning with Wearout Failure Modes
Maintenance Planning with a Constant Failure Rate
Maintenance Planning with Early Failures
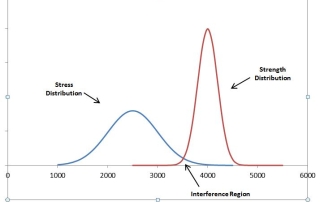
Interference Stress/Strength Analysis
In simplest terms, an item fails when a stress to which it is subjected exceeds the corresponding strength. In this sense, strength can be viewed as “resistance to failure”. Good design practice is such that the strength is always greater than the expected stress. The safety factor “η” can be defined in terms of strength… Read More
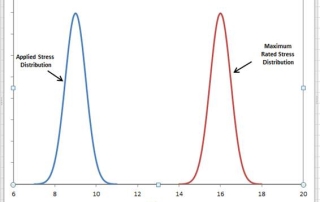
Derating
The practice of limiting electrical, thermal and mechanical stresses on parts to levels below their specified ratings is called derating. MIL-STD-721C offers the following definitions of derating:
Using an item in such a way that applied stresses are below rated values
The lowering of the rating of an item in one stress field to allow an increase… Read More
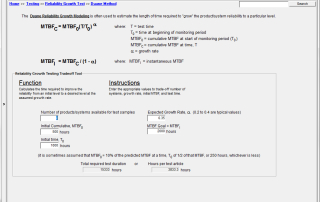
Models Commonly Used to Measure Reliability Growth
Reliability growth is the intentional positive improvement that is made in the reliability of a product or system as defects are detected, analyzed for root cause, and removed. The process of defect removal can be ad hoc, as they are discovered during design and development, a function of an informal test-analyze-and-fix process (TAAF), or it… Read More
How Good Is Your Reliability Approach?
Product reliability is an important discriminator in today’s global marketplace but does your organization know how it’s doing compared to competitors in terms of designing and building reliability into its products? Could/should you be doing more “upfront” reliability activities to improve customer satisfaction, to reduce warranty costs, and to reduce in-plant rework costs? Do you… Read More
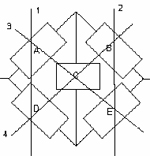
Solving the Complex RBD-Series Parallel System with a Keystone Component
The general form of this type of reliability block diagram has two series circuits in a parallel arrangement combined through a center or “keystone” unit. You are often given the reliability of each block and asked to calculate the reliability of the circuit.
For example let’s say we are given the following five block arrangement pictured… Read More